Internet Capacity
So how much Internet capacity do we need? How many cars you can fit on a road. If you completely fill up a road with cars, the speed of the traffic will grind to a halt. In terms of Internet capacity a completely full road represents our maximum bandwidth capacity measure in bits per second (bps). If our Internet usage is reaching maximum capacity then our Internet connection is fully saturated and no new bits can be placed on the network making the Internet experience for everyone feel very “slow”.
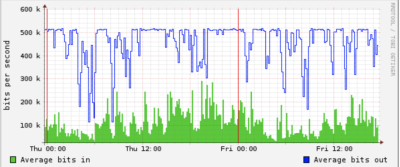
In the above chart the blue graph shows multiple periods of congestion on a 512 kilobits connection that is being fully saturated. In contrast the green graph represents a healthy Internet connection and is one which has spare capacity for new connections to be established. In terms of our road analogy, spare capacity is the space between cars on the highway. The more space between cars, the faster traffic can flow.
 We need enough bandwidth to ensure there is free space.
There are three things that can be done to mitigate a full road 'saturation' scenario.
We need enough bandwidth to ensure there is free space.
There are three things that can be done to mitigate a full road 'saturation' scenario.
- Add more lanes to the road (aka. add bandwidth)
- Meter the flow of traffic with controls such as speed limits and stop lights at intersections (aka. captive portal and usage quotas).
- Educate on how to spot applications that use bandwidth and how to limit the use.

